Business valuation is critical for transactions including fund raising, mergers & acquisitions (M&A), sale of businesses, strategic business decisions like family or shareholders disputes, voluntary value assessment and also for regulatory compliance, tax and financial reporting purposes in India under RBI, Income Tax, Companies Act, SEBI Laws etc. Better Corporate Governance is also leading to requirement of independent Business Valuations.
Though the valuation of a listed company whose shares are actively traded on a nationwide stock exchange in India can be derived from its prevailing market price over a period of time, the valuation of an unlisted company and its shares is the real challenge.
The eligibility to perform valuations also varies under different regulations in India. Recently from 1 February 2019 no one, other than an IBBI “Registered Valuer”, is authorised to conduct valuations under the applicable provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, SEBI ICDR Regulations, 2018 and SEBI (REIT and InvIT) Regulations have also defined Valuer as a person who is registered under section 247 of the Companies Act, 2013.
At the same time the Income Tax Act, 1961 has provision relating to taxability on issue of unquoted equity shares, if issued at a premium. Only a SEBI Registered Merchant Banker is authorised to undertake such valuation by Discounted Free Cash Flow Method.
Thus issue of Equity Shares by a Company may require dual valuation by an IBBI Registered Valuer as well as a SEBI Registered Merchant Banker for meeting regulatory requirements of Companies Act and Income Tax Act respectively. Interestingly, though the Companies Act Valuation requirement is of minimum value, the Income Tax valuation requirement is that of maximum value.
A diagrammatic view of different transactions and applicable valuation requirements under different regulations in India is depicted below:
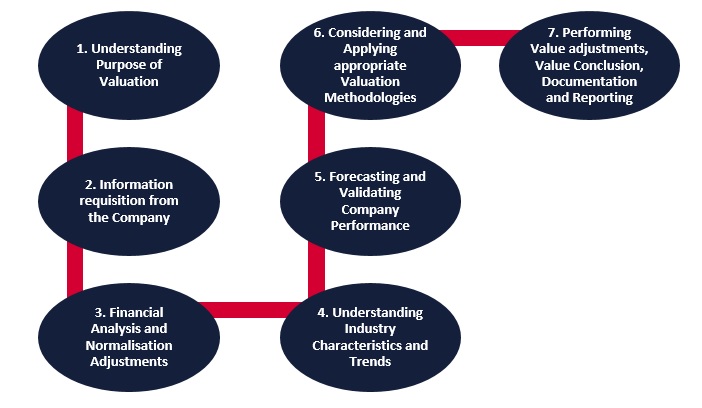
A typical valuation process involves the following steps:
Understanding the purpose of valuation is the first step of the valuation process. Proper analysis of the valuation engagement will assist the valuer in considering, evaluating, and applying the appropriate valuation approaches and methods to the subject interest.
In case valuation is for regulatory or financial reporting purpose, emphasis is to be given on the legal and regulatory aspects which may prescribe a particular valuation methodology and also a particular standard and premise of valuation in some cases. In such a case, the valuer has to undertake the valuation within the defined framework.
All valuations are done at a particular point of time. The valuation date is the specific date at which the valuer estimates the value of the subject interest and concludes on his estimation of value. Date is critical for any valuation engagement as relative valuation (by benchmarking of comparable peer companies or transactions) is heavily dependent on the external market conditions of the industry, economy, etc. on that date.
Concluding Thoughts
It is worth mentioning that even though Valuation is taking place since last six decades in India, however neither there has been any formal Registration of Valuers with any central Authority nor any formal education or training leading to non-standardized valuations. Valuation in itself is evolving in India and is an inexact science.
Section 247 of the Companies Act, 2013 read with Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation) Rules, 2017 (Rules) brought the concept of registered valuers to regulate the practice of valuation of property, stocks, shares, debentures, securities or goodwill or any other assets or net worth of a company or its liabilities in India and to standardize the practice of valuation in line with international standards leading to transparency and better governance.
Valuation is evolving in India and the professional judgment of a valuer is thus critical in any valuation exercise. With effect from February 1, 2019, all valuations required under the Companies Act 2013 and the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) 2016 are conducted through registered valuers.
There are currently only 10 IBBI registered valuer entities and approximately 2200 registered individual valuers in the country.
Corporate Professionals is now covering the full spectrum of valuation services. Corporate Professionals Capital Pvt. Ltd. is a SEBI Registered (Cat-I) Merchant Banker and Corporate Professionals Valuation Services Pvt. Ltd. is an IBBI Registered Valuer entity.